Why every building needs gutter protection
Preventing Flooding
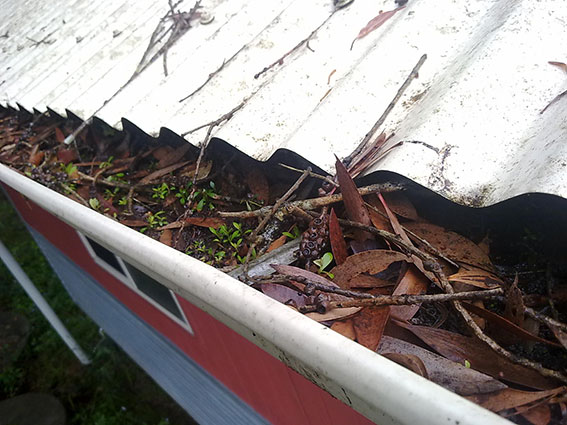
Clogged gutters can cause significant and expensive flood damage to your home or building as water backs up and overflows.

A Hidden Flooding Risk
Gutters clogged with leaves, debris or bird nests present a hidden flooding risk in the event of heavy rain or storms.
With nowhere else to go, water trapped in clogged gutters can overflow into your eaves and ceiling cavities, onto your verandas and terraces, or into your downstairs rooms. This can cost thousands of dollars in repair bills. In fact, water entering homes and buildings from blocked gutters is a leading reason for insurance claims.
Choosing to install gutter mesh to keep leaves, debris and wildlife out of your gutters can help you to avoid the expensive flood damage that can be associated.
Flooding Costs
For home owners, flood damage can result in hefty repair bills, insurance claim hassles and time-consuming clean ups.
Even if the short-term damage seems minimal, there’s the danger of long-term damage to your home’s structural foundations.
Serious health problems can be a result of damp and mould. You may also face incalculable costs such as the heartache that comes from losing irreplaceable items.
For businesses and other organisations, the financial costs of flood damage can mean lost revenue opportunities from interruptions to business continuity.
Considering the costs and hassle that can come from just one leaf too many in your gutters, it’s easy to see why investing in gutter mesh can pay off.
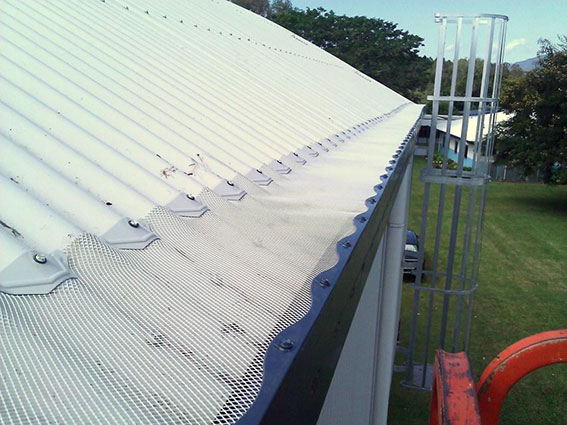


White Rock State School
Large, overhanging trees in a section of White Rock State School created an ongoing flooding problem, as the gutters on a number of buildings were regularly clogged with leaves and overflowed during rain events. This caused significant and costly flood damage each time it occurred. However, as some of these trees were listed with the local council, cutting them down wasn’t a viable solution.
White Rock State School contacted Blue Mountain Co to find a solution to their ongoing flooding problem. After discussing their needs and the buildings’ environment, we recommended that they install our 4mm aluminium gutter mesh.
Since installation, the school’s maintenance manager has reported that they no longer experience any flooding from clogged gutters in these problem areas, leading to significant savings in terms of cost and wasted time. Read the full case study here
Hail & Snow
Accumulated hail or snow can damage your gutters and threaten the integrity of poorly-specified mesh. Hail can also puncture some meshes.
Hail & Snow
When it comes to choosing gutter mesh for your home or building, hail and snow probably aren’t the first things you think about. However, it’s vital that you consider your hail and snow risks in order to choose an appropriate mesh for your location.
During hailstorms, accumulated hail in gutters can cause rainwater to back up and flood your home. By keeping hail out of your gutters, gutter mesh provides protection from this flooding risk.
Heavy hail falling at high speeds can puncture some gutter meshes, while the weight of accumulated hail or snow can cause some gutter meshes to tear. As torn or otherwise damaged gutter mesh can be as bad as having no gutter mesh at all, hail and snow are key environmental factors to consider. The stronger the mesh, the more protected your gutters are.

Hail in Australia
Many areas in Australia are prone to hail, with the Great Dividing Range in eastern Australia the most hail-prone region in the country. In just ten years, between 2007 and 2017, the Bureau of Meteorology recorded nearly 1,000 hail storms. Almost half of these occurred in New South Wales and more than a third occurred in Queensland. Similarly, insurance company Budget Direct’s 2013-2014 hail report found that the top five hail-prone cities in Australia during that year’s storm season were in New South Wales and Queensland.
Hail is a somewhat unpredictable force of nature, but if you live in an area that has experienced hail before, you should consider choosing a stronger gutter mesh. Definitely look for something that can withstand puncturing and the weight of accumulated hail.
For help choosing the right gutter mesh for your property’s environment, we recommend using our Mesh Matcher tool.
Snow in Australia
People don’t often associate snow with Australia, but many Australians do live in snow-prone areas such as the Snowy Mountains in NSW and elevated parts of Tasmania. You probably know whether your home or property is located in a snow-prone area. If you are, you’ll want to ensure you choose a gutter mesh that can withstand the weight of accumulated snow and won’t collapse or tear under the strain.
To give you an idea: depending on its water content, snow can be surprisingly heavy. A square metre of 10cm deep snow weighs between 10 and nearly 100kg – a pretty significant weight to bear.
For help choosing the right gutter mesh for your property’s environment, we recommend using our Mesh Matcher tool.

Safety
Gutter cleaning represents a significant safety risk for home owners and workplaces. Minimising your cleaning requirements will also minimise your safety risks.
Gutter Cleaning Safety Risks
Falls from height such as falls from ladders and roofs are one of the most common causes of work-related and DIY death and injury in Australia. On average, 19.4 Australians – mostly men aged over 50 – die every year after falling from a ladder. Thousands more are injured. Some are permanently disabled.
As an “at-height” activity, gutter maintenance poses both a significant residential safety and workplace health and safety risk, with a human and financial cost no family, organisation or building manager wants to bear. Bigger buildings and buildings that are prone to clogged gutters pose the greatest safety risks, as they require the most extensive or regular gutter cleaning.
Installing a gutter mesh gutter guard to keep leaves, animals and debris out of your gutters is a recognised solution for minimising gutter maintenance requirements and the safety risks that accompany this task.
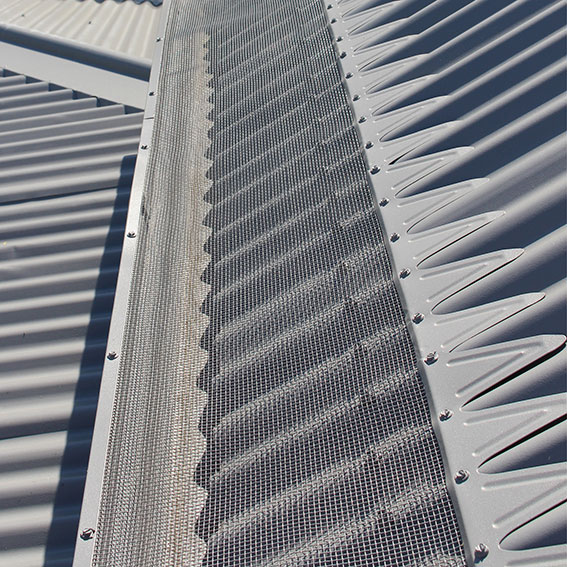


How gutter mesh helps
Gutter mesh is installed over your gutters as a gutter guard to keep leaves, animals and debris out. On sloped roofs, it’s installed in line with your roof slope to maximise leaf blow-off.
By keeping your gutters virtually leaf- and debris-free, gutter mesh significantly reduces your gutter maintenance requirements. In turn, this reduces the risks of gutter maintenance for you, your family members or your staff. And as gutter maintenance becomes significantly less frequent, it’s also easier to justify hiring a professional to take care of the task for you.
It’s important to remember that for best results, you need to match your mesh to the size of the leaves in your area. While all gutter mesh still requires minimal maintenance, the wrong size mesh create an additional maintenance burden as leaves get stuck in the mesh or even pass through.
Our free Mesh Matcher tool provides custom mesh recommendations for the right gutter mesh for your property based on leaf size and other key factors, so you can enjoy the benefits of minimal maintenance gutter mesh should entail. To find your ideal gutter guard, use our Mesh Matcher.
Maintenance & safety case study
Low pitch roofs, large box gutters and overhanging gum trees created an ongoing maintenance problem for staff at the University of Southern Queensland Toowoomba campus.
Having previously experienced extensive and expensive flood damage to campus buildings and equipment due to blocked gutters, maintenance staff were required to climb up on roofs and clean out gutters once a fortnight – a significant working from heights risk.

Pests and Vermin
Animals in your gutters can wreak havoc to your home or building – especially if they use your gutters as an entry point to your roof cavity.

True price of pests in your gutters
Animals in your gutters are more than just an annoyance. Pests in your gutters can cause extensive damage, health hazards and serious disruptions to your day-to-day life or business operations.
These problems are only exacerbated if the animals use your gutters as a convenient access point to your roof and wall cavities. The cost of pest removal and repairing pest-related damage is never cheap, and if you do nothing to stop these animals returning, it’s a cost you’ll pay again and again.
By forming a physical barrier against pests of all shapes and sizes, gutter mesh helps prevent infestations and ensure you won’t have to pay the true price of pests in your gutters.
Keep pests out of your roof
- Noise (pests running around and using the space as a nest or to raise their young)
- Mess and destruction (pests leaving droppings, damaging your insulation and internal structure, or even dying and decomposing in your roof)
- Removal expenses (pests often require specialists to set traps and relocate them)


Stop pests nesting in your gutters & eliminate insect havens
By stopping birds, possums and other pests from nesting in your gutters during the dry season, you’ll prevent blocked pipes and flooding. For homes with rainwater tanks, keeping pests out also helps to prevent contaminated rainwater.
Accumulated leaves in your gutters can lead to pooled water that endangers your home and health by attracting insects, including mosquitoes. Keeping leaves out of your gutters with gutter mesh helps to prevent mosquitoes breeding in this stagnant gutter water and spreading mosquito-borne diseases.
Both steel and aluminium gutter mesh provide an affective barrier to entry of pests and vermin.
Rain Harvesting
If you have a Rain Harvesting system, keeping your gutters free of potential contaminants is a key step towards harvesting cleaner rainwater and lots of it.
Gutter Mesh & Rain Harvesting
Harvesting clean rainwater – and lots of it – is the ultimate goal for any Rain Harvesting system.
To achieve this goal, it’s necessary to keep potential contaminants such as leaves, vegetation, pests and pest-related debris out of your pipes and rainwater tank. And that’s where gutter mesh comes in.


How it works
Installing gutter mesh is an effective first step in limiting potential contaminants that may otherwise end up in your rainwater tank.
The mesh forms a physical barrier over your gutters that keeps leaves, pests and other debris out, while still letting rainwater in.
This not only helps you to harvest cleaner rainwater – it also helps maximise the volume you can harvest, and protects your post-tank pumps by reducing the volume of sediment in your rainwater tank.
Why keep leaves and pests out?
Leaves, vegetation and pests can all clog your gutters and downpipes, reducing the volume of rainwater that ends up in your tank.
Leaves, vegetation and pests can also compromise your water’s opacity, colour and odour.
Gutters clogged with leaves or pest detritus can also lead to pooled water that attracts the smallest pests of all, mosquitoes. These pests can seriously affect the health of your entire Rain Harvesting system (and your home, too).

Protect your Gutter from Leaves
Leaves that fall into your gutters come in many shapes and sizes. Vegetation that glides off a well-chosen mesh may pass through or get stuck in less suitable options, so it’s important to consider the size of the leaves in your area.
Why leaf size matters
Not all mesh will keep out all plant matter. That’s because different species of tree produce different sized leaves, flowers, berries and filaments. So similarly, gutter mesh comes in different apertures (hole sizes).
To match the right mesh, we encourage you to classify the smallest size leaves and vegetation in your gutters and around your home into one of the categories below.
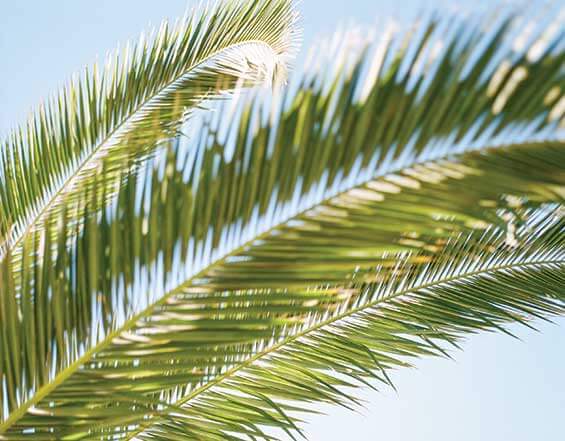


Know your leaf size
To match the right mesh for your property, you should classify the smallest size leaves and vegetation in your gutters (or around your property) into one of these four categories:
- Needles (pine needles or similar)
- Small leaves and fine foliage (wattle, jacaranda, poinciana, leopard tree leaves etc.)
- Medium leaves (silky oak, gum leaves, gumnuts, etc.)
- Large leaves (palm fronds, bamboo, etc.)
Armed with this information, you can use the table below as a rough guide to identify the right size mesh for your leaves. Alternatively, you can use our Mesh Matcher tool to find the right mesh to suit your leaf size. Mesh Matcher asks six simple questions about your property and environment in order to recommend the best mesh or meshes for you. Use it for free now.
Why leaves matter
Leaves are the root cause of many gutter-related problems, including gutter cleaning safety risks and costs, clogged gutters and expensive flood damage, and heightened bushfire risks.
These problems can affect homes, schools, businesses and commercial buildings alike.
Considering the potentially huge financial and human cost of these problems, it’s easy to see why it pays to invest in gutter mesh to keep leaves out of your gutters.


Prevent flooding and reduce cleaning costs and safety risks
Clogged gutters and downpipes can cost you thousands in the event of heavy rain or storms, as water overflows into your eaves and ceiling cavities, onto your verandas and terraces or into your downstairs rooms. In fact, water entering homes from blocked gutters is a leading reason for insurance claims.
As well as the risks of flooded gutters, gutter cleaning is a dirty and dangerous job. The cost of professional cleaning can quickly add up, while the risk of serious injury or even death from DIY gutter cleaning is uncomfortably high. By installing the right gutter mesh, you can significantly reduce these risks and expenses.
Help your rain harvesting system
If you have a rainwater tank, keeping plant matter out of your gutters is a big step towards the ultimate goal of having cleaner rainwater and lots of it. Without mesh, leaves can contaminate your rainwater supply or reduce the volume of water flowing into your tank.
Steel and aluminium gutter mesh are both effective to keeping out plant matter so long as the appropriate aperture has been selected.

Bushfire and Ember Guard
Poorly-specified gutter mesh may put your property at risk from bushfire by letting leaves into your gutters or letting embers through the gaps between your guttering and roof.
Bushfire & ember guarding
The vast majority of homes destroyed during bushfires are victims of ember attack, meaning they ignite and burn due to contact with windborne embers (burning debris) rather than direct flame contact.
Your gutters are a prime source of such ember attacks. They make you vulnerable to ember attack in two significant ways – by providing easy fuel for embers, and by offering embers easy entry to roof cavity.
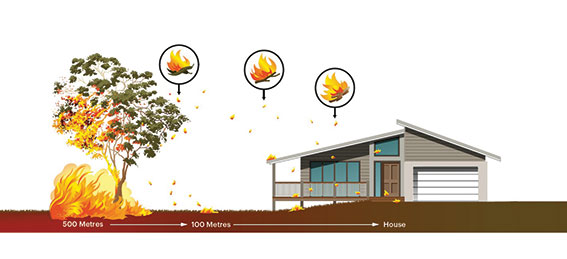

Vulnerability to embers
1. Inside your gutters
Dry leaves in gutters are a source of fuel that can be ignited by bushfire embers. Unprotected gutters and poorly specified gutter mesh are the main reason for this problem; however, poorly-specified gutter mesh can also leave you vulnerable to this threat by allowing leaves to enter your gutters.
2. Inside your building
Embers can get inside your building through small gaps between your roof, gutters and fascia. They can then start a fire when they land on insulation or other fuel sources. Only a gutter mesh made from materials approved to the Australian standard AS3959-2009 such as corrosion-resistant steel, and with an aperture of 2mm or smaller, will keep embers out of your gutters.
Understanding bushfire compliance
AS3959–2009
Australian Standard AS3959-2009 Construction of buildings in bushfire prone areas, mandates different construction requirements based on your property’s BAL (Bushfire Attack Level).
Designed to improve the ability of new homes to withstand bushfire and ember attack, the standard affects your choice of construction materials for a number of features around your home, including gutter guards such as gutter mesh.
Ember guard compliance
Ember guards stop burning embers getting into your home through gaps greater than 3mm. They can be made from a non-combustible mesh with an aperture (hole size) of 2mm or smaller. Mandatory for all new homes built in a bushfire-prone area with a BAL of 12.5 or higher, they’re used to “seal” any gaps greater than 3mm, such as gaps around your roof sheeting.
For homes in areas with a BAL of 12.5, 19 or 29, ember guards can be manufactured from corrosion-resistant steel, bronze or aluminium. For homes in areas with a BAL of 40 or higher, only corrosion-resistant steel or bronze ember guards are allowed. Corrosion-resistant steel gutter mesh with an aperture of 2mm is an ideal ember guard solution.
Gutter guard compliance
According to AS3959–2009, gutter guards are optional for anyone building a new home in an area with a BAL of 12.5, 19, 29, 40 or FZ. However, if you choose to use them, the standard states: “if installed, gutter guards shall be non-combustible”. All Blue Mountain Co Gutter Mesh is non-combustible and complies to the Australian standards.
Most gutter guards are NOT ember guards, but Blue Mountain Co 2mm steel mesh is both an ember guard and gutter guard. It is compliant with both requirements.


Bushfire Guard vs Ember guard
The reality is not all ‘bushfire compliant’ gutter mesh products are actually ‘ember guard compliant’. At Blue Mountain Co, we know you must protect yourself against the risk of fires igniting in any area of your property, including your gutters, roof cavities and wall spaces.
This means using the correctly-specified products. Only “ember guard compliant” mesh will keep both leaves and embers out of your gutters, providing maximum defence against ember attack. That’s why we recommend our 2mm steel gutter mesh for all homes in bushfire-prone areas.
Rust & Corrosion
Avoiding mixing “dissimilar” metals, minimise time of wetness and ensure that you use fit-for-purpose, specially coated steel to manage the risk of corrosion of your roof, gutters or mesh.
Rust & corrosion
- Not mixing different kinds of metals
- Minimising the total time metal surfaces are wet
- Using fit-for-purpose, specially coated steel


Avoiding Mixing Metals
Minimise Wetness
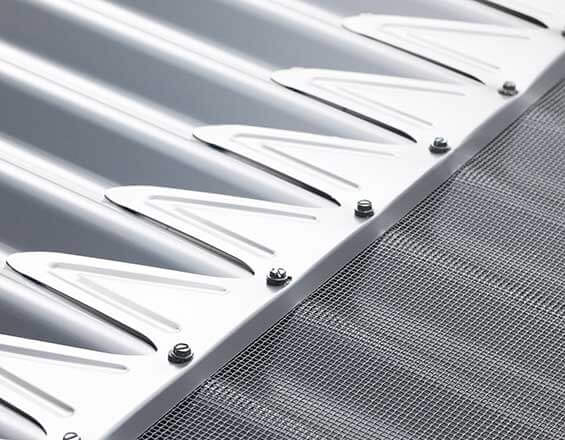


Use Fit-For-Purpose, Specially Coated Steel
Galvanised steel, COLORBOND® steel, zinc-coated steel and stainless steel are all examples of specially coated steels that are rust-resistant. However, it is important to choose a rust-resistant steel that is fit for purpose. Avoid mixing dissimilar metals by selecting the rust-resistant steel that is most compatible with your roof and gutter materials.
What about stainless steel?
In and of itself, stainless steel is a rust-resistant material. However, when joined to a roof made from a different material, such as COLORBOND® steel, it can cause your roof to rust prematurely. If you are considering stainless steel, it is important to ensure that the roof and gutter materials are compatible and not dissimilar.
Choose the right material for you
Choosing the correct material type is really important when doing anything on the roof to avoid corrosion. Our aluminium and steel gutter mesh products are suitable for most roof types in Australia and New Zealand.
However, if you would like advice to suit your roof and situation, you can talk to our gutter mesh specialists on (07) 3248 9600, by emailing [email protected] or by filling in this form

Reduce Maintenance Costs
Installing gutter mesh is a great way to save on gutter maintenance & other gutter-related costs for homes, schools & commercial buildings.
Maintenance costs
Your gutters may seem like one of the plainest features on your home or building, but they can actually cost you dearly. Regular gutter maintenance and cleaning can represent a significant ongoing cost for home owners, schools and commercial building managers.
On the other hand, failure to maintain your gutters comes with its own costs, including the risk of expensive flood damage. Even if your gutters are kept leaf and debris free, they may still attract animals and pests, with all the associated costs of removal or repair this can bring.
However, by installing an appropriate gutter mesh around your home or building, you can keep leaves, pests and other debris out of your gutters to significantly reduce the costs and hassles of gutter maintenance and avoid expensive gutter-related problems.


Calculating your savings
To calculate the savings and economic return that will accompany installing gutter mesh on your building, simply add up the money you spend on gutter maintenance each year, compare this to the cost of installation, and calculate how long it will take for the savings to match your investment.
By keeping your gutters basically debris-free, gutter mesh significantly reduces the frequency at which maintenance is required. For example, if you own a small home that costs you $1,000 a year for quarterly gutter cleaning, installing gutter mesh could cut this expense down to $250 a year. The cost and return for larger homes and buildings is likely to be even greater.
It’s worth keeping in mind that this calculation doesn’t consider the savings you’ll enjoy from preventing expensive gutter-related problems such as clogging, flooding and pest invasion. By taking this into account too, it’s even clearer that installing gutter mesh on your home or building makes good economic sense.
Maintenance savings case study
With an 8 metre high roof and a number of surrounding trees that dropped leaves and debris into its gutters, the multi-purpose hall at Yorkeys Knob State School required professional cleaning once a quarter, costing the school $4,000 a year.
After installing Blue Mountain Co’s steel gutter mesh on the multi-purpose hall, the school was able to significantly reduce the frequency of gutter cleaning – without worrying about the risk of clogged gutters and expensive flood damage.
As such, they enjoyed a full return on investment in less than 2 years, with significant ongoing savings in the future. Download the full Case Study here.
